Contact Changfu Chemical Now!
+86 27 8439 6550 | +86 181 6277 0058
Monomers and Polymers: Everything You Need to Know
Monomers and polymers are pivotal in both natural and synthetic material sciences, underpinning the construction of a wide array of everyday items. This blog delves into the intricate relationship between monomers and polymers, exploring their formation processes, distinctive properties, and diverse applications across industries.
Understanding Monomers
Monomers are elemental building blocks, typically small molecules with functional groups that enable them to form covalent bonds with other monomers. These units are crucial in polymer synthesis, wherein the repetitive linking of monomers results in the creation of polymers. Consider some notable examples of monomers:
- Ethylene (C2H4): Foundation of polyethylene, widely used in packaging and containers.
- Styrene (C8H8): Basis of polystyrene, utilized in insulation and packaging materials.
- Vinyl Chloride (C2H3Cl): Principal component of polyvinyl chloride (PVC), integral to piping and construction materials.
- Amino Acids: Essential components in protein synthesis, forming chains that dictate biological functions.
![]()
The Polymerization Process
Addition Polymerization: This mechanism involves the sequential attachment of monomers without the expulsion of any by-products. It's exemplified by the production of polyethylene, where ethylene molecules polymerize into long chains.
Condensation Polymerization: Unlike addition polymerization, this process entails the coupling of monomers accompanied by the release of small molecules, typically water or alcohol. Nylon synthesis, which combines diamines and dicarboxylic acids, is a prime illustration of condensation polymerization.
Properties and Applications of Polymers
Properties of Polymers:
- Versatility: Polymers exhibit a broad spectrum of properties ranging from flexibility to rigidity, determined by the nature and arrangement of their constituent monomers.
- Durability: Many polymers are resistant to chemical degradation, enhancing their suitability for various applications.
- Lightweight: Their low density makes polymers ideal for industries requiring lightweight materials.
Applications of Polymers:
- Packaging: Polyethylene and polypropylene dominate this sector due to their resilience and cost-effectiveness.
- Construction: PVC finds extensive use in pipes, windows, and flooring owing to its robustness and adaptability.
- Textiles: Polyesters and nylons are prevalent in textile manufacturing, offering durability and ease of maintenance.
- Medical: Biocompatible polymers like polylactic acid (PLA) are used in surgical sutures and implants, facilitating tissue regeneration.
- Automotive: Polymers contribute to vehicle weight reduction and design flexibility, benefiting components from bumpers to interior panels.
Monomers and Polymers in Everyday Life
Polymers are indispensable in our daily lives, found in countless products and applications that enhance convenience, safety, and functionality. Let's explore some specific examples of monomers and polymers that are integral to everyday life.
Household Items
Plastic Bottles and Containers:
- Polymer: Polyethylene terephthalate (PET)
- Monomer: Ethylene glycol + Terephthalic acid
- Properties: Lightweight, durable, and recyclable.
- Application: Used for water bottles, food containers, and packaging materials. PET’s high strength-to-weight ratio makes it ideal for beverage containers, offering both durability and recyclability.
Food Storage Wrap:
- Polymer: Polyvinyl chloride (PVC)
- Monomer: Vinyl chloride
- Properties: Flexible, transparent, and strong.
- Application: Used in cling films to preserve food freshness. The flexibility and transparency of PVC make it perfect for wrapping food items, ensuring they remain fresh while providing an easily recognizable view of the contents.
Textiles and Clothing
Synthetic Fabrics:
- Polymer: Polyester
- Monomer: Ethylene glycol + Terephthalic acid
- Properties: Durable, resistant to shrinking and stretching.
- Application: Used in clothing, upholstery, and industrial fabrics. Polyester’s durability and resistance to environmental factors make it a popular choice in the fashion and textile industries, providing long-lasting and easy-care fabrics.

Nylon:
- Polymer: Nylon 6,6
- Monomer: Hexamethylenediamine + Adipic acid
- Properties: Strong, elastic, and resistant to wear.
- Application: Used in hosiery, activewear, and ropes. Nylon’s strength and elasticity make it suitable for a wide range of applications, from clothing to industrial uses, where resilience and flexibility are essential.
Medical Applications
Biodegradable Sutures:
- Polymer: Polylactic acid (PLA)
- Monomer: Lactic acid
- Properties: Biocompatible, biodegradable.
- Application: Used in surgical sutures that gradually dissolve in the body. PLA’s biocompatibility ensures that it safely interacts with body tissues, while its biodegradability eliminates the need for suture removal, enhancing patient comfort and reducing medical procedures.
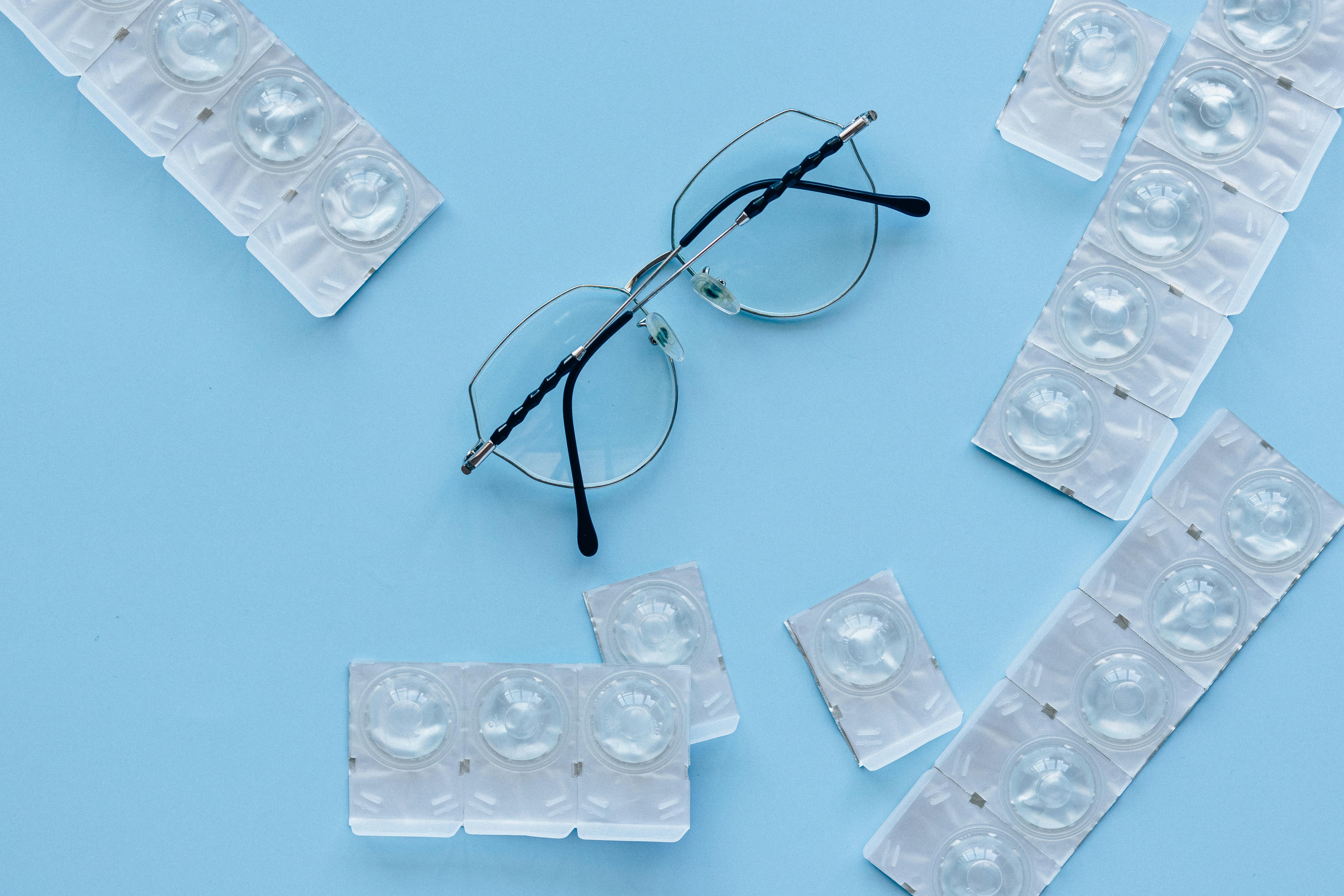
Contact Lenses:
- Polymer: Poly(methyl methacrylate) (PMMA)
- Monomer: Methyl methacrylate
- Properties: Clear, rigid, and biocompatible.
- Application: Used in hard contact lenses. PMMA’s clarity and rigidity make it an excellent material for vision correction, providing a durable and comfortable alternative to traditional glasses.
Construction Materials
PVC Pipes:
- Polymer: Polyvinyl chloride (PVC)
- Monomer: Vinyl chloride
- Properties: Durable, resistant to corrosion and chemicals.
- Application: Used in plumbing, electrical insulation, and construction materials. PVC’s resistance to environmental degradation and chemical reactions makes it a reliable material for piping and construction, ensuring long-lasting infrastructure.
Insulation Foam:
- Polymer: Polystyrene (PS)
- Monomer: Styrene
- Properties: Lightweight, good thermal insulator.
- Application: Used in insulation for buildings and packaging. Polystyrene’s insulating properties make it essential for maintaining temperature control in buildings and protecting delicate items during transport.
Automotive Industry
Car Parts:
- Polymer: Polypropylene (PP)
- Monomer: Propylene
- Properties: Tough, resistant to fatigue and impact.
- Application: Used in bumpers, dashboards, and interior components. Polypropylene’s toughness and resistance to impact make it ideal for automotive applications, where durability and safety are paramount.
Tires:
- Polymer: Styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR)
- Monomer: Styrene + Butadiene
- Properties: High abrasion resistance, good aging stability.
- Application: Used in the manufacturing of car tires. SBR’s abrasion resistance and stability under various conditions ensure that tires provide safe and reliable performance over their lifespan.
Key Insights and Conclusion
Monomers and polymers constitute the bedrock of contemporary materials science, exemplifying the intricate balance between molecular structure and practical application. Their synergy drives innovation across sectors, facilitating advancements in technology, healthcare, and environmental sustainability. By comprehending the interplay between monomers and polymers, one gains deeper insight into the materials that define our world.
For a deeper exploration into specific polymer applications, visit our resource on methyl methacrylate polymer.
Wrapping Up
Monomers and polymers embody the essence of material diversity and functionality, epitomizing the transformative potential of molecular engineering. Whether in industry or nature, their significance underscores a dynamic field of research and application.
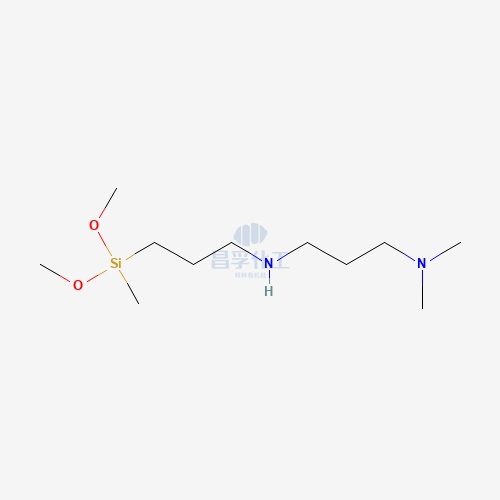
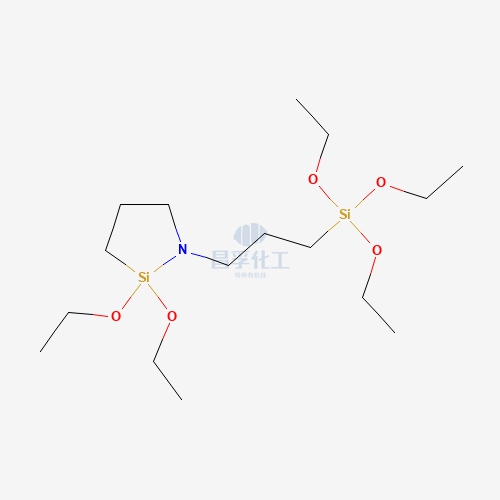
Popular Silicon Compounds
Popular Silicon Compounds
Related News & Blog
Related News & Blog






























































































+86 27 8439 6550
+86 181 6277 0058
sales@cfsilanes.com
Optics Valley Bio-City
No. 666, Gaoxin Avenue
Hongshan District, Wuhan City

+86 27 8439 6550 | +86 181 6277 0058
sales@cfsilanes.com
Optics Valley Bio-City
No. 666, Gaoxin Avenue
Hongshan District, Wuhan City
Copyright © Hubei ChangFu Chemical Co., Ltd. All Rights



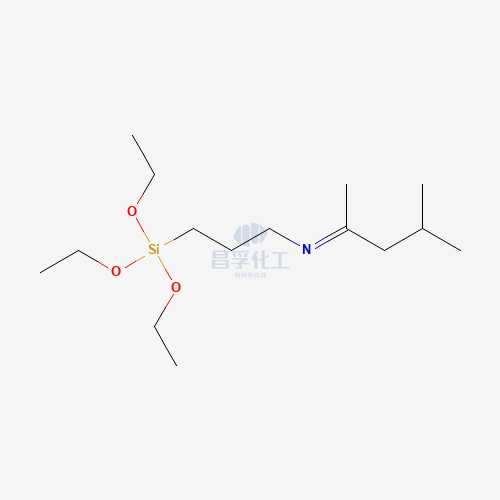
![N-[5-(Trimethoxysilylpropyl)-2-aza-1-oxopentyl]caprolactam CAS: 106996-32-1 106996 32 1 N-[5-(Trimethoxysilylpropyl)-2-aza-1-oxopentyl]caprolactam CAS: 106996-32-1 106996 32 1](https://cdn.yofishseo.com/1363882761272232/106996-32-1.jpg)