Contact Changfu Chemical Now!
+86 27 8439 6550 | +86 181 6277 0058
Silicones - Formula, Structure, Properties, and Applications
Introduction
Silicones are a unique class of synthetic materials that combine the properties of both organic and inorganic compounds. Their versatility and stability make them indispensable in various industries. This blog explores the formula, structure, properties, and wide-ranging applications of silicones.
Formula of Silicones
Silicones are generally represented by the formula (R2SiO)n, where 'R' stands for organic groups like methyl, ethyl, or phenyl. The silicon-oxygen backbone gives silicones their unique properties, while the organic groups determine their specific characteristics.
Structure of Silicones
The fundamental structure of silicones consists of a repeating unit of siloxane (−R2Si−O−SiR2−). This silicon-oxygen backbone is flexible and can form linear, cyclic, or cross-linked structures. The organic groups attached to the silicon atoms vary, leading to different types of silicones:
- Linear Silicones: These have a straight-chain structure, commonly used in lubricants and hydraulic fluids.
- Cyclic Silicones: These form ring structures, often found in personal care products like shampoos and conditioners.
- Cross-linked Silicones: These have a three-dimensional network structure, ideal for high-strength applications like sealants and adhesives.
Properties of Silicones
Silicones are renowned for their exceptional properties, which make them suitable for a wide range of applications:
- Thermal Stability: Silicones can withstand extreme temperatures, ranging from -60°C to +300°C, without degrading. This property is crucial for applications in automotive and aerospace industries.
- Hydrophobicity: Silicones repel water, making them ideal for waterproofing applications in construction and electronics.
- Flexibility: Silicones remain flexible over a wide temperature range, which is essential for applications requiring durable, yet flexible materials, like medical tubing.
- Electrical Insulation: Silicones are excellent insulators, making them essential in the manufacture of cables, connectors, and other electrical components.
- Chemical Resistance: Silicones resist many chemicals, including acids and bases, which is vital for applications in harsh chemical environments.
![]()
What are the Applications of Silicones?
Silicones' unique properties make them suitable for a broad range of applications across various industries:
Medical: Silicones are widely used in the medical field due to their biocompatibility, flexibility, and stability.
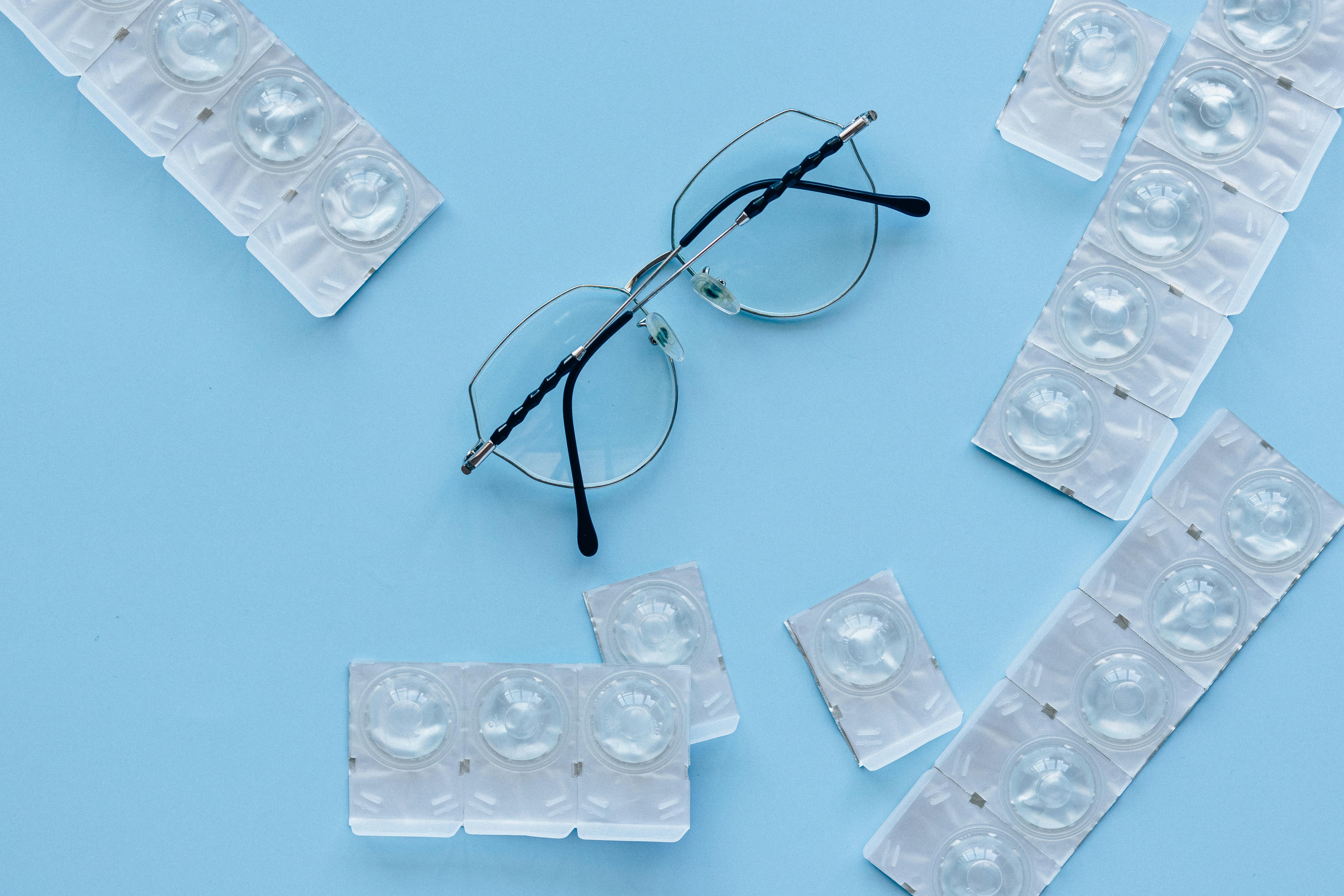
- Silicone Hydrogel Contact Lenses: Allow more oxygen to pass through to the cornea, enhancing comfort for wearers. According to a study published in the Journal of Contact Lens Research and Science, silicone hydrogel lenses provide up to 5 times more oxygen permeability than conventional hydrogel lenses.
- Silicone Implants: Used in breast implants, cochlear implants, and artificial joints. Silicone breast implants, for example, have a lower rupture rate compared to saline implants. Data from the American Society of Plastic Surgeons indicate that silicone implants are preferred by 84% of patients.
- Medical Tubing: Silicone is used in catheters and drug delivery systems due to its flexibility and biocompatibility. Silicone catheters are preferred in many medical procedures as they are less likely to cause allergic reactions compared to latex catheters.
Automotive: Silicones are employed in the automotive industry for their durability, resistance to extreme conditions, and versatility.
- Gaskets and Seals: Provide long-lasting seals that can withstand extreme temperatures and pressures. Silicone gaskets are used in engine components to ensure tight seals and prevent leaks.
- Lubricants: Silicone-based lubricants are used in various automotive components for their stability and performance. They are commonly used in brake systems and in lubricating door locks and hinges.
- Spark Plug Boots: Silicone rubber is used for its high dielectric strength and heat resistance, ensuring reliable performance in the ignition system.
Electronics: In electronics, silicones are essential in insulating materials, adhesives, and coatings due to their electrical insulation properties.
- Insulating Materials: Used in cables, connectors, and other components to provide electrical insulation. Silicone insulation ensures that cables and wires can operate safely in high-temperature environments.
- Conformal Coatings: Silicone coatings protect circuit boards from moisture, dust, and other environmental factors. These coatings ensure the longevity and reliability of electronic devices.
- Encapsulants: Silicone encapsulants protect electronic components from mechanical stress and environmental damage. A report from Electronics Weekly shows that silicone encapsulants can extend the lifespan of electronic devices by up to 30%.
Construction: Silicones are used in construction for their weather resistance, durability, and flexibility.
- Sealants: Used in glazing and weatherproofing applications to provide durable, flexible seals. Silicone sealants are commonly used for sealing joints in buildings and bridges, ensuring long-lasting protection against water infiltration.
- Adhesives: Silicone adhesives bond various materials, including glass, metal, and plastics. These adhesives are crucial in the assembly of building facades and window installations.
- Coatings: Silicone-based coatings protect surfaces from weathering, corrosion, and UV radiation. These coatings are used on building exteriors to enhance durability and appearance.
Consumer Products: Silicones are found in a variety of consumer products for their non-toxic and flexible nature.
- Personal Care: Found in shampoos, conditioners, and skin care products for their conditioning properties. Silicones like dimethicone create a smooth, silky feel on the skin and hair.
- Kitchenware: Silicone molds, baking mats, and utensils are popular for their non-stick properties and heat resistance. Silicone bakeware is microwave and dishwasher safe, making it a convenient choice for home cooks.
- Textiles: Silicone softeners improve the softness and feel of fabrics. For more information on silicone softeners, visit silicone softeners. Silicone coatings are also used on fabrics to make them water-repellent and durable.
Aerospace: Silicones play a crucial role in the aerospace industry due to their high-temperature stability and reliability.
- Thermal Protection Systems: Used in spacecraft to protect against extreme temperatures during re-entry. Silicones help insulate and protect critical components from the intense heat.
- Seals and Gaskets: Provide reliable seals in aircraft engines and other critical components, ensuring safety and performance at high altitudes.
Energy: Silicones contribute to the energy sector by enhancing the efficiency and durability of various components.
- Solar Panels: Silicone materials are used in the encapsulation of photovoltaic cells to protect against environmental damage. Silicone sealants ensure that solar panels remain watertight and durable.
- Wind Turbines: Silicone sealants and coatings protect turbine blades from weathering and wear, enhancing their longevity and performance.
Food and Beverage: Silicones are safe for use in food and beverage applications due to their inertness and compliance with safety standards.
- Bakeware: Silicone bakeware is popular for its non-stick properties and heat resistance. Silicone molds and baking mats are used in both professional and home kitchens for their ease of use and cleaning.
- Seals and Gaskets: Used in food processing equipment for their inertness and compliance with food safety standards. Silicone seals ensure that food processing equipment operates hygienically and efficiently.
Industrial: Silicones are used in industrial applications for their high-temperature stability, low friction, and durability.
- Lubricants and Greases: Silicone-based lubricants are used in machinery for their high-temperature stability and low friction. These lubricants reduce wear and tear on moving parts, extending the lifespan of industrial equipment.
- Mold Release Agents: Silicones are used to prevent sticking in molding processes, ensuring smooth release of molded parts and reducing defects.
Textiles: Silicones enhance the performance and feel of textile products.
- Coatings: Silicone coatings are applied to fabrics to make them water-repellent and durable. These coatings are used in outdoor gear and protective clothing to enhance performance in harsh conditions.
- Softening Agents: Silicones are used to soften fabrics and improve their feel, making clothes more comfortable to wear.
Paper and Film: Silicones improve the performance of paper and film products.
- Release Coatings: Silicone release coatings are applied to paper and film to prevent sticking and improve handling. These coatings are used in labels, tapes, and packaging materials to ensure smooth processing and application.
Main Differences Between Silicone and Other Polymers
Silicone polymers stand out from other polymers primarily due to their unique chemical structure. While most common polymers, like polyethylene or polystyrene, have a carbon-based backbone, silicones are based on a silicon-oxygen backbone (Si-O-Si) with organic groups such as methyl or phenyl attached to the silicon atoms. This distinct structure imparts silicones with superior thermal stability, allowing them to maintain their properties over a wide temperature range from -60°C to 300°C. In contrast, many other polymers tend to have lower thermal stability and may degrade at higher temperatures. Additionally, the flexibility of the Si-O bond in silicones ensures that they remain highly flexible even at low temperatures, whereas other polymers can become brittle.
Another key difference is chemical resistance. Silicones are notably resistant to water, oxygen, ozone, and many chemicals, making them suitable for various harsh environments. Other polymers exhibit a wide range of chemical resistance, with some being vulnerable to degradation when exposed to certain substances. Biocompatibility is another area where silicones excel. They are often used in medical devices and implants due to their non-reactivity with biological tissues. In comparison, the biocompatibility of other polymers varies, and some may require additional treatments or coatings to be safely used in medical applications.
Synthesis of Silicones in Industrial Processes
The industrial synthesis of silicones typically begins with the hydrolysis and condensation of chlorosilanes, such as dimethyldichlorosilane. During this process, chlorosilanes are hydrolyzed to form silanols, which then condense to produce siloxane polymers. Polymerization is then carried out using catalysts, often platinum-based, to control the reaction and achieve the desired polymer structure. The ratio of monomers and reaction conditions can be adjusted to produce various silicone products, including oils, rubbers, and resins.
For silicone rubbers, cross-linking is an essential step. This involves using vulcanization or curing agents, such as peroxides or platinum catalysts, to cross-link the polymer chains, enhancing their mechanical properties. The ability to fine-tune these processes allows manufacturers to create silicones with specific characteristics tailored to different applications, from flexible seals to durable coatings.
Unique Properties of Silicones
Silicones possess a range of unique properties that make them versatile across numerous applications. One of their standout features is their ability to remain stable and functional over a wide temperature range, from -60°C to 300°C. This thermal stability, combined with their inherent flexibility and elasticity, ensures that silicones maintain their performance under varying conditions. Additionally, silicones exhibit excellent chemical resistance, making them resilient against water, oils, and solvents.
Their electrical insulation properties are also notable, with silicones providing excellent dielectric performance, making them ideal for electrical insulation. Moreover, silicones are highly resistant to UV radiation and ozone, which contributes to their durability in outdoor applications. Another critical property is their biocompatibility, which makes them safe for use in medical devices and implants due to their non-reactivity with biological tissues.
Role of Silicones in the Aerospace Industry
In the aerospace industry, silicones play a crucial role due to their exceptional properties. They are used in thermal protection systems for spacecraft, leveraging their high thermal stability to provide insulation against extreme temperatures. Silicones also offer reliable sealing and bonding solutions for aircraft and spacecraft components, maintaining integrity under the rigorous conditions of high altitude and space travel. Their ability to dampen vibrations helps reduce mechanical stresses on aerospace structures, enhancing the longevity and reliability of components.
Silicone coatings protect surfaces from environmental damage, including UV radiation, moisture, and chemicals, which is vital for the longevity of aerospace equipment. Additionally, the flexibility of silicones ensures that seals and gaskets maintain their performance in dynamic environments, accommodating movements and maintaining airtight seals.
Contribution of Silicones to the Efficiency of Solar Panels
Silicones contribute significantly to the efficiency and durability of solar panels. They are used for encapsulating solar cells, protecting them from moisture, dust, and mechanical damage, thereby enhancing the panels' lifespan. The optical clarity of silicones ensures maximum light transmission to the solar cells, which is crucial for optimizing energy conversion. Additionally, silicones aid in thermal management by dissipating heat, preventing overheating, and maintaining the efficiency of the solar cells.
In the construction of solar panels, silicones serve as adhesives and sealants, securing components and providing durable seals that withstand environmental exposure. Their flexibility allows them to accommodate the thermal expansion and contraction of solar panel components, preventing stress and potential damage. These properties make silicones indispensable in ensuring the long-term performance and reliability of solar panels.
Conclusion
Silicones are a vital part of modern technology and everyday life. Their unique combination of properties makes them irreplaceable in many applications, from medical devices to automotive components and electronics. Understanding the formula, structure, properties, and applications of silicones helps appreciate their importance in various fields.
By leveraging the versatility of silicones, industries can develop innovative solutions that enhance performance, durability, and safety. Whether in high-tech medical devices or everyday consumer products, silicones continue to revolutionize how we live and work.
For more information on how silicones are used in home and living products, check out silicone softeners.
Popular Silicon Compounds
Popular Silicon Compounds
Related News & Blog
Related News & Blog






























































































+86 27 8439 6550
+86 181 6277 0058
sales@cfsilanes.com
Optics Valley Bio-City
No. 666, Gaoxin Avenue
Hongshan District, Wuhan City

+86 27 8439 6550 | +86 181 6277 0058
sales@cfsilanes.com
Optics Valley Bio-City
No. 666, Gaoxin Avenue
Hongshan District, Wuhan City
Copyright © Hubei ChangFu Chemical Co., Ltd. All Rights



![N-[5-(Trimethoxysilylpropyl)-2-aza-1-oxopentyl]caprolactam CAS: 106996-32-1 106996 32 1 N-[5-(Trimethoxysilylpropyl)-2-aza-1-oxopentyl]caprolactam CAS: 106996-32-1 106996 32 1](https://cdn.yofishseo.com/1363882761272232/106996-32-1.jpg)