Contact Changfu Chemical Now!
+86 27 8439 6550 | +86 181 6277 0058
The Science Behind Silicone Polymer: Properties, Benefits, and Applications
Silicone polymer, a class of synthetic materials with unique properties, has become a staple in various industries, including healthcare, electronics, construction, and consumer goods. Its remarkable flexibility, heat resistance, chemical stability, and biocompatibility set it apart from other polymers. In this blog, we will explore the science behind silicone polymer, from its molecular structure and synthesis to its practical applications. We'll also highlight the benefits of this versatile material and discuss why it has become so important in modern technology and manufacturing.
![]()
What is Silicone Polymer?
At its core, silicone polymer is a type of elastomeric polymer made from a combination of silicon (a natural element found in sand and quartz), oxygen, carbon, and hydrogen. The key distinguishing feature of silicone polymer is its backbone, made of alternating silicon and oxygen atoms with organic side chains attached to the silicon. This backbone gives silicone polymers their unique properties, making them highly versatile across different applications.
Understanding Silicone Monomer
To understand silicone polymer, we must first look at its building block, silicone monomer. The basic unit of a silicone polymer is known as a "silicone monomer," which typically consists of one silicon atom bonded to various organic groups, such as methyl (–CH3) or vinyl (–CH=CH2), and linked to oxygen atoms. This structure forms the basis for the larger polymer chain, as these monomers react with each other in a process called polymerization.
The primary monomer for silicone polymers is usually dimethylsiloxane (DMS), which forms long chains through condensation reactions. During this reaction, water molecules are released as a byproduct, and the monomers link together, forming a continuous silicone backbone. The resulting polymer is highly flexible, stable, and resistant to environmental stresses, including temperature extremes and exposure to chemicals.
Properties of Silicone Polymer
Silicone polymers possess several distinct properties that make them invaluable in various industries. These properties arise from the material's unique molecular structure, particularly the alternating silicon-oxygen backbone, which imparts high flexibility and stability. Below, we will explore some of the most important properties that define silicone polymers.
1. Thermal Stability
Silicone polymers are well-known for their exceptional thermal stability, allowing them to function effectively in a wide temperature range. They can withstand temperatures as low as –60°C and as high as 300°C without significant degradation. This makes them ideal for applications in extreme environments, such as automotive and aerospace industries, where materials are exposed to high heat and cold.
2. Flexibility and Elasticity
The flexibility of the silicone backbone gives these polymers remarkable elasticity, allowing them to stretch and bend without breaking. This property is especially useful in applications requiring durable seals, gaskets, and medical devices. Unlike other materials, silicone polymers can maintain their flexibility across a wide temperature range, making them highly reliable in both cold and hot conditions.
3. Chemical Resistance
One of the major advantages of silicone polymers is their resistance to chemicals, including oils, solvents, and acids. This property is particularly valuable in industrial applications where exposure to harsh chemicals is common, such as in chemical processing plants, laboratories, and automotive parts. Silicone polymers can withstand prolonged contact with chemicals without deteriorating or losing their integrity.
4. Water Resistance
Silicone polymers are highly hydrophobic, meaning they repel water and resist moisture absorption. This water resistance is vital in applications like sealants, waterproof coatings, and electrical insulations, where exposure to water or humidity could otherwise compromise performance. The hydrophobic nature also makes silicone polymers suitable for use in medical devices and healthcare products, where cleanliness and moisture resistance are crucial.
5. Biocompatibility
Silicone polymers are known for their biocompatibility, making them safe for use in medical devices and implants. They do not react with biological tissues, which is why they are used in prosthetics, catheters, and even cosmetic implants. The inertness of silicone makes it less likely to cause allergic reactions or infections, and its durability ensures long-lasting performance in the human body.
6. Electrical Insulation
Silicone polymers also excel as electrical insulators. Their high dielectric strength and resistance to electrical breakdown make them ideal for use in electronics, where they are used as protective coatings, insulators, and encapsulants. In particular, silicone polymers are valuable in environments where electrical components must be protected from moisture, dust, and extreme temperatures.
7. Low Toxicity
Unlike many other synthetic materials, silicone polymers exhibit low toxicity, making them safe for use in food-grade applications, cookware, and baby products. They do not release harmful chemicals when heated or exposed to other environmental conditions, making them a preferred choice in industries that prioritize health and safety.
Benefits of Silicone Polymer
The unique properties of silicone polymers offer numerous benefits, which contribute to their widespread use across multiple sectors. Below, we highlight some of the key benefits:
1. Durability
Silicone polymers are extremely durable, able to withstand harsh conditions such as high temperatures, chemical exposure, and mechanical stress. This durability translates into longer product lifespans and reduced maintenance costs, which is especially important in industrial and commercial applications.
2. Versatility
Thanks to their wide range of properties, silicone polymers can be formulated to suit a variety of applications, from soft, flexible rubbers to hard, durable plastics. This versatility allows manufacturers to tailor silicone materials to specific requirements, whether for medical devices, automotive parts, or consumer electronics.
3. Environmental Resistance
Silicone polymers are highly resistant to environmental factors like UV radiation, ozone, and oxidation. This environmental resistance makes them suitable for outdoor applications, such as coatings for solar panels, outdoor electronics, and building materials, where long-term exposure to the elements is a concern.
4. Non-Stick Properties
Silicone's natural non-stick surface makes it ideal for use in cookware, baking mats, and industrial molds. This property also reduces the need for chemical coatings, enhancing the material's safety and ease of use in food-related applications.
5. Sustainability
Although silicone is a synthetic material, it is considered more environmentally friendly compared to some other polymers. Silicone polymers have long lifespans, and their durability reduces the need for frequent replacements, contributing to a sustainable lifecycle. Additionally, some silicone products can be recycled, although recycling facilities for silicone are not as common as for traditional plastics.
Silicone Polymer Applications
Given their impressive properties and numerous benefits, silicone polymers are used in a wide range of applications. Below, we outline some of the key industries where silicone polymers play a critical role:
1. Medical Industry
The medical industry relies heavily on silicone polymers for a variety of devices and applications. These include catheters, surgical implants, wound dressings, and prosthetic devices. Silicone's biocompatibility and flexibility make it ideal for use in devices that come into contact with the human body, while its durability ensures long-term performance.
In cosmetic surgery, silicone implants are commonly used due to their soft, natural feel and biocompatibility. Additionally, silicone adhesives and gels are used in wound care for their ability to promote healing without causing skin irritation.
2. Electronics and Electrical Insulation
In the electronics industry, silicone polymers are used as protective coatings, sealants, and insulators. Silicone's ability to withstand high temperatures and protect against moisture and dust makes it invaluable for safeguarding sensitive electronic components. Silicone is also used in cable insulation and encapsulation of electronic circuits.
3. Automotive Industry
In automotive manufacturing, silicone polymers are used in various seals, gaskets, hoses, and O-rings. These parts are exposed to high heat, chemicals, and mechanical stress, making silicone the ideal material for maintaining durability and performance under harsh conditions. Silicone polymers also reduce noise and vibration in automotive applications, contributing to a smoother driving experience.
4. Construction Industry
Silicone polymers are extensively used in the construction industry for sealing and insulating buildings. They are applied in weatherproofing windows and doors, as well as sealing joints in concrete and glass structures. The material's excellent adhesion, flexibility, and resistance to UV light make it ideal for outdoor applications, where long-term exposure to the elements is inevitable.
5. Consumer Products
Silicone polymers are widely used in consumer products, including kitchenware, baby products, and personal care items. Silicone baking mats, spatulas, and molds have gained popularity due to their non-stick surfaces and heat resistance. In baby care, silicone pacifiers and bottle nipples are prized for their safety and durability. Personal care products, such as silicone-based hair serums and skin moisturizers, benefit from the material's hydrophobic and skin-friendly properties.
6. Aerospace and Aviation
The aerospace industry requires materials that can withstand extreme temperatures, pressures, and environmental stresses. Silicone polymers are used in various components, such as gaskets, seals, and insulation for aircraft, spacecraft, and satellites. Their ability to function in extreme conditions makes them an ideal choice for high-performance aerospace applications.
7. Textile and Fashion
Silicone polymers are used in the textile industry to enhance fabrics with properties like water repellency, softness, and stretchability. Silicone coatings are applied to outdoor gear, sportswear, and fashion garments to improve durability and comfort.
![]()
Conclusion
Silicone polymer stands out as one of the most versatile and valuable materials in modern industry due to its exceptional properties, including thermal stability, flexibility, chemical resistance, and biocompatibility. The science behind this material, starting with the silicone monomer, explains its ability to meet the demanding requirements of various applications, from healthcare and electronics to construction and consumer goods.
As industries continue to innovate, the demand for high-performance materials like silicone polymer is only expected to grow. With its unique blend of properties, silicone polymer offers solutions that traditional polymers cannot, making it indispensable in a wide range of fields.
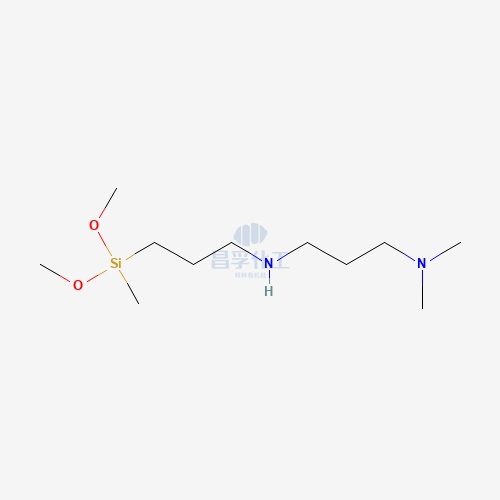
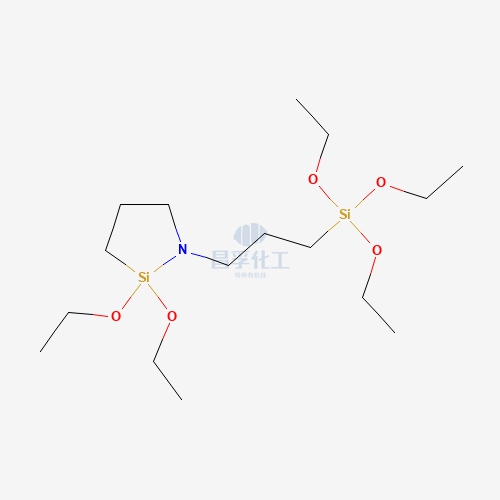
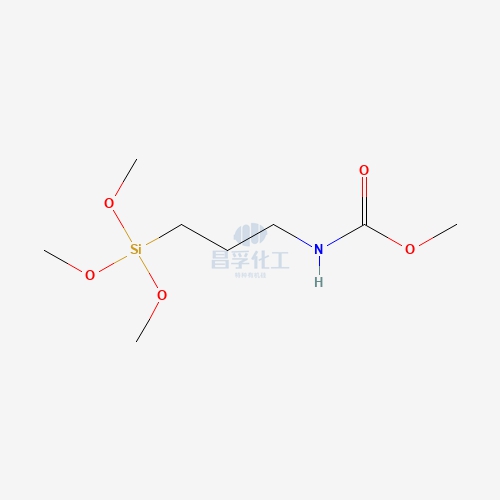
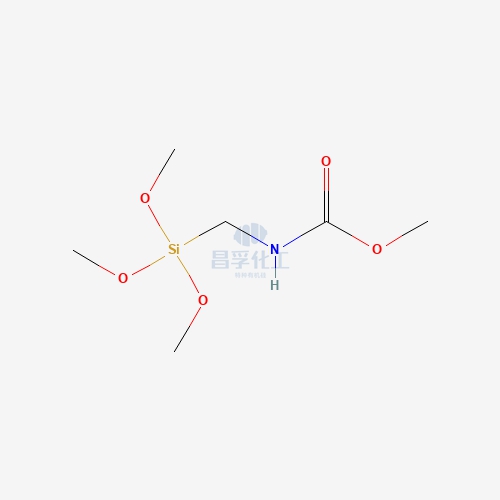
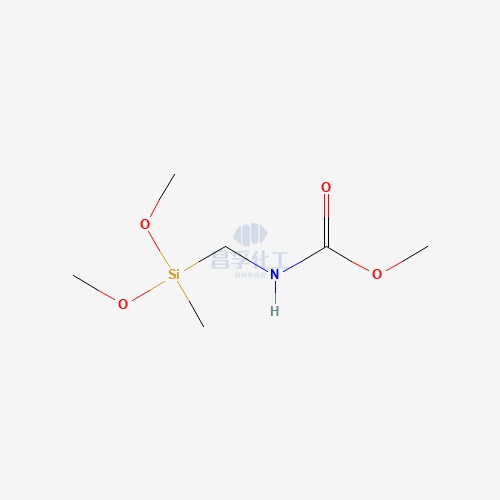
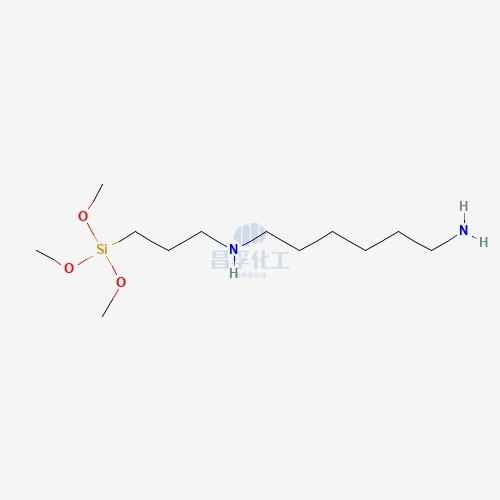
Popular Silicon Compounds
Popular Silicon Compounds
Related News & Blog
Related News & Blog






























































































+86 27 8439 6550
+86 181 6277 0058
sales@cfsilanes.com
Optics Valley Bio-City
No. 666, Gaoxin Avenue
Hongshan District, Wuhan City

+86 27 8439 6550 | +86 181 6277 0058
sales@cfsilanes.com
Optics Valley Bio-City
No. 666, Gaoxin Avenue
Hongshan District, Wuhan City
Copyright © Hubei ChangFu Chemical Co., Ltd. All Rights



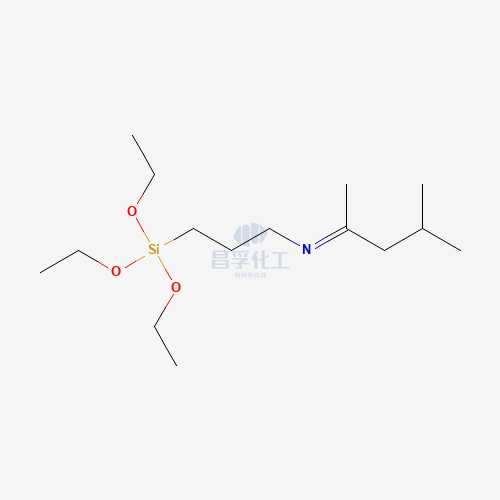
![N-[5-(Trimethoxysilylpropyl)-2-aza-1-oxopentyl]caprolactam CAS: 106996-32-1 106996 32 1 N-[5-(Trimethoxysilylpropyl)-2-aza-1-oxopentyl]caprolactam CAS: 106996-32-1 106996 32 1](https://cdn.yofishseo.com/1363882761272232/106996-32-1.jpg)