Contact Changfu Chemical Now!
+86 27 8439 6550 | +86 181 6277 0058
Specialty Silanes
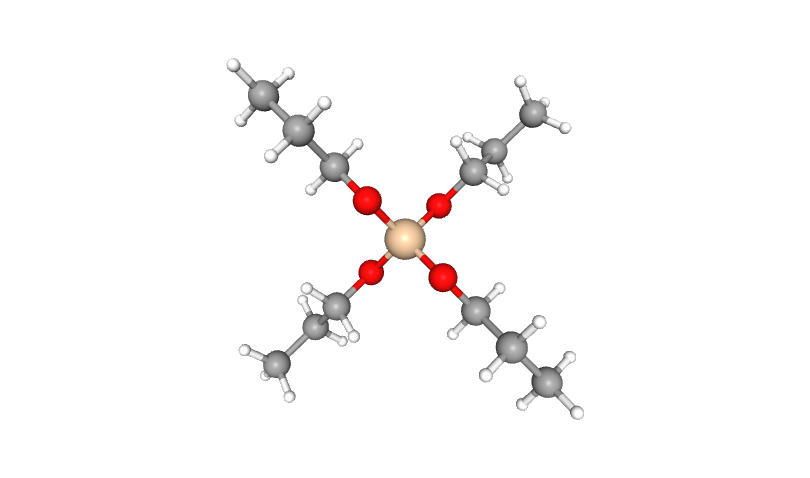
Specialty silanes are a type of silane monomer that replaces certain groups in a silane molecule with functional groups with specific applications via chemical reactions. The molecular structure of specialty silanes comprises particular active groups that can react with certain materials to form chemical bonds and perform specific functions.

Specialty Silanes
Specialty silanes are a type of silane monomer that replaces certain groups in a silane molecule with functional groups with specific applications via chemical reactions. The molecular structure of specialty silanes comprises particular active groups that can react with certain materials to form chemical bonds and perform specific functions.
Types of Specialty Silanes
Types of Specialty Silanes
Specialty silanes are classified into the following categories based on functional groups in their molecular structure:
Amino specialty silanes: They have a chemical structure that includes amino functional groups such as primary, secondary, or tertiary amines. They can increase adhesion and are compatible with hydrogen-containing polymers well.
Epoxy specialty silanes: Their molecular structure includes epoxy groups. Epoxy groups are reactive, meaning they can react with other groups found in polymers, like carboxyl groups and anhydrides.
Mercapto specialty silanes: These silanes have sulfhydryl functional groups in their molecular structure, allowing them to react with polymers containing sulfur, phosphorus, and other elements.
Olefin specialty silanes: These silanes have olefin functional groups in their molecular structure, allowing them to react with unsaturated bond materials.
Methacryloyloxy specialty silanes: These silanes have methacryloyloxy functional groups in their molecular structure and can react with materials that have double bonds.
In addition to the categories listed above, specialized silanes also include cyano silanes, isocyanate silanes, halogen silanes, phenyl silanes, and silylating reagents.
Specialty silanes are classified into the following categories based on functional groups in their molecular structure:
Amino specialty silanes: They have a chemical structure that includes amino functional groups such as primary, secondary, or tertiary amines. They can increase adhesion and are compatible with hydrogen-containing polymers well.
Epoxy specialty silanes: Their molecular structure includes epoxy groups. Epoxy groups are reactive, meaning they can react with other groups found in polymers, like carboxyl groups and anhydrides.
Mercapto specialty silanes: These silanes have sulfhydryl functional groups in their molecular structure, allowing them to react with polymers containing sulfur, phosphorus, and other elements.
Olefin specialty silanes: These silanes have olefin functional groups in their molecular structure, allowing them to react with unsaturated bond materials.
Methacryloyloxy specialty silanes: These silanes have methacryloyloxy functional groups in their molecular structure and can react with materials that have double bonds.
In addition to the categories listed above, specialized silanes also include cyano silanes, isocyanate silanes, halogen silanes, phenyl silanes, and silylating reagents.
Properties of Specialty Silanes
Properties of Specialty Silanes
- High adhesion: Specialty silanes can form chemical bonds with the surfaces of inorganic substrates, resulting in good adhesion.
- Weather resistance: Specialty silanes are chemically and weather resistant, allowing them to function well in harsh environments.
- Anti-fouling: Special silane may prevent a variety of surface stains and has good anti-fouling properties.
- Waterproof: Special silane may fix silane molecules on the surface of the material via surface penetration, resulting in excellent waterproof performance.
- Corrosion resistance: Special silane is very corrosion resistant and can function in acidic or alkaline settings.


- High adhesion: Specialty silanes can form chemical bonds with the surfaces of inorganic substrates, resulting in good adhesion.
- Weather resistance: Specialty silanes are chemically and weather resistant, allowing them to function well in harsh environments.
- Anti-fouling: Special silane may prevent a variety of surface stains and has good anti-fouling properties.
- Waterproof: Special silane may fix silane molecules on the surface of the material via surface penetration, resulting in excellent waterproof performance.
- Corrosion resistance: Special silane is very corrosion resistant and can function in acidic or alkaline settings.
What is the Difference between Specialty Silanes and Conventional Silane Coupling Agents?
What is the Difference between Specialty Silanes and Conventional Silane Coupling Agents?

Compared to conventional silane coupling agents, Changfu specialty silanes have:
Higher functionality: Specialty silanes have a distinct chemical structure and functional groups, making them more reactive and useful. This enables these silanes to better satisfy the requirements of specific applications while also achieving higher performance.
Better stability: Specialty silanes have higher thermal and chemical stability and can withstand a wider variety of temperatures and chemical conditions. This makes special silanes more suitable for usage in high-temperature, high-humidity, or corrosive conditions.
Stronger adhesion: Because of their unique chemical structure and functional groups, specialty silanes can generate stronger chemical bonds and physical adsorption with other materials, resulting in improved adherence. This extends the life and reliability of products including inks, coatings, adhesives, and sealants.
Higher production efficiency: Specialty silanes are often more reactive and controllable, allowing for faster and more efficient chemical processes. This contributes to increased manufacturing efficiency, shorter production cycles, and lower costs.

Compared to conventional silane coupling agents, Changfu specialty silanes have:
Higher functionality: Specialty silanes have a distinct chemical structure and functional groups, making them more reactive and useful. This enables these silanes to better satisfy the requirements of specific applications while also achieving higher performance.
Better stability: Specialty silanes have higher thermal and chemical stability and can withstand a wider variety of temperatures and chemical conditions. This makes special silanes more suitable for usage in high-temperature, high-humidity, or corrosive conditions.
Stronger adhesion: Because of their unique chemical structure and functional groups, specialty silanes can generate stronger chemical bonds and physical adsorption with other materials, resulting in improved adherence. This extends the life and reliability of products including inks, coatings, adhesives, and sealants.
Higher production efficiency: Specialty silanes are often more reactive and controllable, allowing for faster and more efficient chemical processes. This contributes to increased manufacturing efficiency, shorter production cycles, and lower costs.
News & Blog in Changfu Chemical
News & Blog in Changfu Chemical






































































































+86 27 8439 6550
+86 181 6277 0058
sales@cfsilanes.com
Optics Valley Bio-City
No. 666, Gaoxin Avenue
Hongshan District, Wuhan City

+86 27 8439 6550 | +86 181 6277 0058
sales@cfsilanes.com
Optics Valley Bio-City
No. 666, Gaoxin Avenue
Hongshan District, Wuhan City
Copyright © Hubei ChangFu Chemical Co., Ltd. All Rights