Contact Changfu Chemical Now!
+86 27 8439 6550 | +86 181 6277 0058
Organosilicon Compounds: Everything You Need to Know
Exploring Organosilicon Compounds
Introduction to Organosilicon Compounds
Organosilicon compounds represent a fascinating and versatile class of chemicals, playing crucial roles in both industrial applications and everyday products. These compounds, which consist of silicon atoms bonded to organic groups, have unique properties that make them indispensable in fields ranging from electronics to cosmetics. This blog will delve into what organosilicon compounds are, their structure, types, synthesis, and wide-ranging applications.
Chemical Structure of Organosilicon Compounds
At the heart of organosilicon chemistry is the silicon-carbon (Si-C) bond. Silicon, a group 14 element, shares similarities with carbon but differs significantly in its chemical behavior due to its larger atomic size and lower electronegativity. The Si-C bond imparts unique characteristics to organosilicon compounds, such as thermal stability, hydrophobicity, and flexibility, distinguishing them from purely organic or inorganic compounds.
Unlike carbon, which can form stable double and triple bonds with other elements, silicon typically forms stable single bonds. This difference leads to the formation of structures like silanes (Si-H), siloxanes (Si-O-Si), and silicones (polysiloxanes), each with distinct properties and applications.
Types of Organosilicon Compounds
Organosilicon compounds can be categorized into several types based on their structure and applications:
Silicones
Silicones are perhaps the most well-known organosilicon compounds. They are polymers with repeating units of siloxane (Si-O-Si) chains, giving them remarkable flexibility and heat resistance.
-
Linear Silicones: These have a straight-chain structure and are used in applications such as lubricants, sealants, and adhesives due to their excellent stability and flexibility.
-
Cyclic Silicones: These silicones form ring structures and are commonly used in cosmetics and personal care products for their smooth texture and spreadability
Siloxanes
Siloxanes are a subgroup of silicones, consisting of alternating silicon and oxygen atoms. They form the backbone of many silicone polymers.
-
Polysiloxanes: These are long chains of siloxane units and are widely used in medical devices, contact lenses, and implants due to their biocompatibility and flexibility.
-
Cyclosiloxanes: These are cyclic compounds used in skin and hair care products, providing a silky feel without leaving a greasy residue.
Silanes
Silanes are simpler organosilicon compounds with the general formula R-SiH3, where R is an organic group. They serve as important intermediates in the production of more complex organosilicon compounds.
-
Functionalized Silanes: These silanes have additional functional groups, making them useful as coupling agents in coatings and adhesives.
-
Alkyl Silanes: These are used as water repellents and surface modifiers in construction materials and textiles.
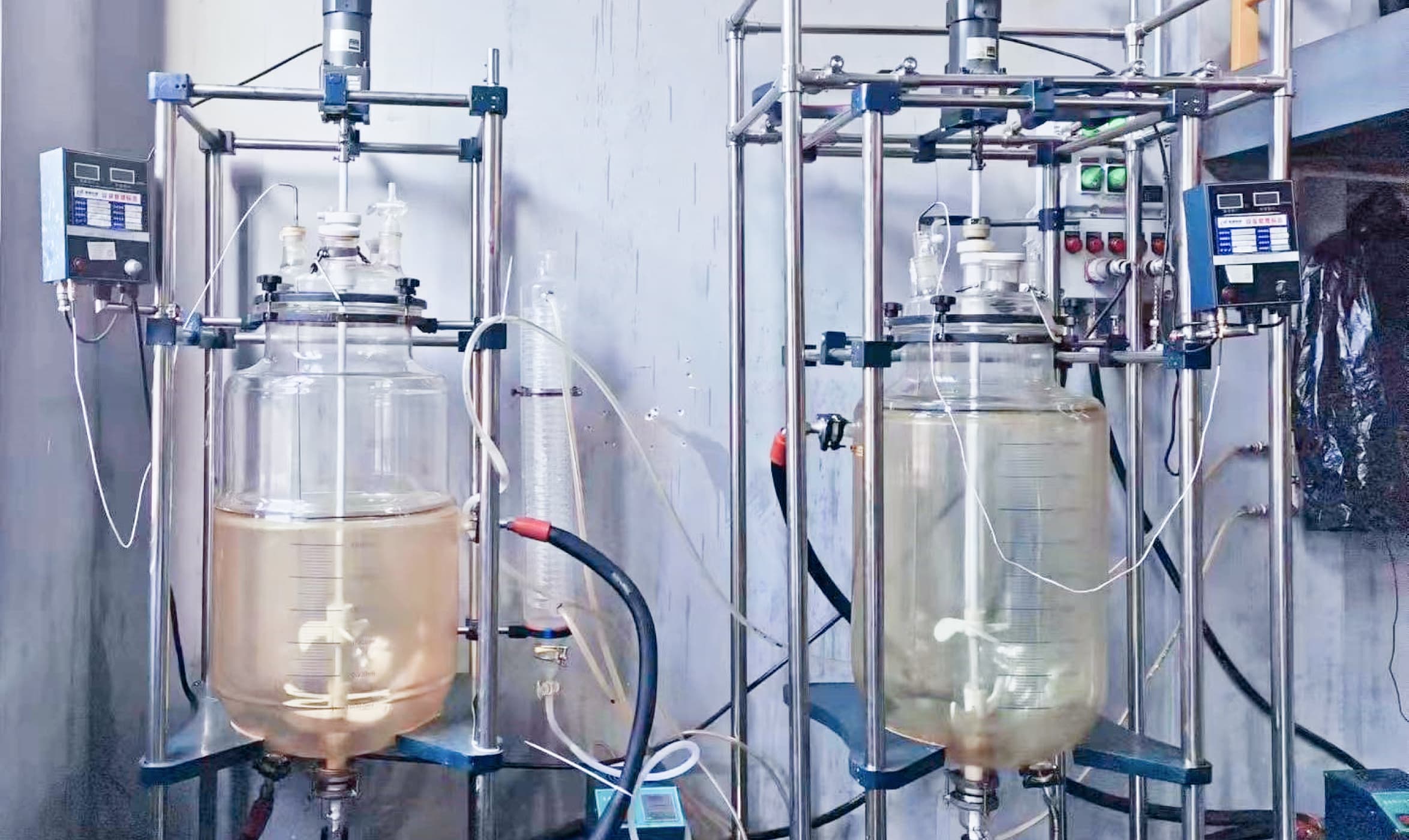
Synthesis of Organosilicon Compounds
The synthesis of organosilicon compounds involves several key methods, each tailored to produce specific types of compounds:
-
Grignard Reactions: A common method for introducing organic groups onto silicon, involving the reaction of silicon halides with Grignard reagents.
-
Hydrosilylation: This reaction involves the addition of a silicon-hydrogen bond across an unsaturated carbon-carbon bond, widely used in the production of silicones.
-
Direct Process (Rochow Process): This industrial process involves the reaction of elemental silicon with methyl chloride to produce methyl chlorosilanes, which are then hydrolyzed to form silicones.
![]()
Applications of Organosilicon Compounds
Organosilicon compounds are incredibly versatile and are used in a wide array of applications across various industries:
Industrial Applications
-
Silicone Rubber: Used in automotive, aerospace, and consumer goods due to its durability, heat resistance, and flexibility.
-
Sealants and Adhesives: Silicones provide excellent bonding and sealing properties, making them ideal for construction and electronics.
Consumer Products
-
Cosmetics and Personal Care: Cyclosiloxanes and other silicones are used in products like shampoos, conditioners, and skin creams for their smoothing and hydrating properties.
-
Medical Devices: Due to their biocompatibility, organosilicon compounds are used in implants, prosthetics, and medical tubing.
Specialized Uses
-
Electronics: Silicones are used as insulating materials in electronic components, protecting against moisture and thermal damage.
-
Coatings: Silanes and silicones are used in paints and coatings for their protective properties and ability to enhance adhesion.
-
Pharmaceuticals: Organosilicon compounds are used as excipients and drug delivery agents due to their unique chemical properties.
Environmental and Health Considerations
While organosilicon compounds offer numerous benefits, their environmental and health impacts are important considerations. Many organosilicon compounds, particularly silicones, are not readily biodegradable, leading to concerns about their accumulation in the environment. However, they are generally considered to be of low toxicity, though certain siloxanes have raised concerns due to their persistence and potential bioaccumulation.
Regulations vary by region, but the safety of organosilicon compounds is generally well-regulated, especially in consumer products like cosmetics and medical devices.
Recent Advances in Organosilicon Chemistry
Recent developments in organosilicon chemistry have focused on improving the synthesis processes, developing new materials, and expanding applications:
-
Innovations in Synthesis: New catalytic methods and greener synthesis routes are being developed to produce organosilicon compounds more efficiently and sustainably.
-
New Applications in Technology: Advances in nanotechnology and electronics have driven the development of new organosilicon materials with enhanced properties, such as improved thermal stability and conductivity.
-
Organosilicon Compounds in Green Chemistry: There is a growing interest in using organosilicon compounds in sustainable chemistry, particularly in the development of environmentally friendly materials and processes.
Comparison with Other Organometallic Compounds
Organosilicon compounds are often compared to other organometallic compounds, such as organotitanium and organostannane compounds:
-
Organosilicon vs. Organotitanium: Organosilicon compounds tend to be more thermally stable and resistant to oxidation than organotitanium compounds, making them more suitable for high-temperature applications.
-
Organosilicon vs. Organostannane: Organosilicon compounds are generally less toxic and more environmentally friendly than organostannanes, which are often used in anti-fouling paints but pose significant environmental risks.
-
Advantages of Organosilicon Compounds: The unique combination of flexibility, thermal stability, and biocompatibility makes organosilicon compounds highly advantageous in a wide range of applications.
Future Trends in Organosilicon Research
The future of organosilicon research is promising, with several trends emerging:
-
Potential in Sustainable Chemistry: Organosilicon compounds are being explored for their potential in creating sustainable materials, such as biodegradable silicones and eco-friendly coatings.
-
Development of Biocompatible Materials: Advances in biotechnology and medical research are driving the development of new organosilicon materials for use in implants, drug delivery systems, and other medical applications.
-
Future Applications in Nanotechnology: The unique properties of organosilicon compounds make them ideal candidates for nanotechnology applications, including in the development of nanoscale electronics and sensors.
Challenges in Organosilicon Compound Development
Despite their advantages, organosilicon compounds face several challenges:
-
Synthetic Challenges: Developing new synthetic methods that are efficient, scalable, and environmentally friendly remains a significant challenge.
-
Stability Issues: While many organosilicon compounds are stable, some are prone to hydrolysis or oxidation, limiting their use in certain applications.
-
Market Adoption Barriers: High production costs and competition from other materials can hinder the adoption of organosilicon compounds in new markets.
Key Scientists and Discoveries in Organosilicon Chemistry
The field of organosilicon chemistry has been shaped by the contributions of several key scientists:
-
Friedrich Wöhler: Known for early discoveries in organosilicon chemistry, including the first synthesis of an organosilicon compound in 1857.
-
Eugene G. Rochow: Developed the Direct Process, a crucial industrial method for producing organosilicon compounds, revolutionizing the silicone industry.
-
Modern Contributions: Recent advancements have been driven by ongoing research into new materials, synthesis methods, and applications, particularly in the fields of medicine and electronics.
FAQs About Organosilicon Compounds
-
What are the primary uses of organosilicon compounds?
- Organosilicon compounds are used in a wide range of applications, including industrial products (e.g., silicone rubber), consumer goods (e.g., cosmetics), and specialized fields (e.g., electronics).
-
How are organosilicon compounds synthesized?
- Common methods include Grignard reactions, hydrosilylation, and the Direct Process (Rochow Process).
-
Are organosilicon compounds environmentally friendly?
- While many are considered low in toxicity, concerns exist regarding their biodegradability and environmental persistence.
-
What makes organosilicon compounds unique compared to other organometallic compounds?
- Their unique silicon-carbon bond provides properties like thermal stability, flexibility, and hydrophobicity, distinguishing them from other organometallic compounds.
-
What are some common products containing organosilicon compounds?
- Common products include silicone sealants, lubricants, cosmetics, medical devices, and electronic components.
-
How are organosilicon compounds regulated?
- Regulations vary by region, but they are generally subject to safety assessments, particularly in consumer products like cosmetics and medical devices.
Conclusion
Organosilicon compounds are integral to many aspects of modern life, from industrial manufacturing to personal care products. Their unique properties, driven by the silicon-carbon bond, make them highly versatile and valuable. As research continues, we can expect to see even more innovative uses and advancements in this field, particularly in sustainable chemistry and high-tech applications.
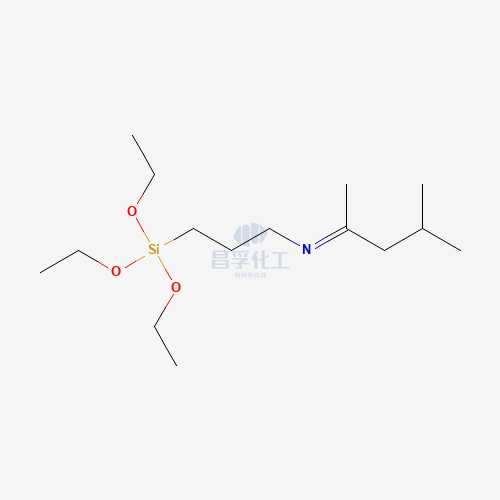
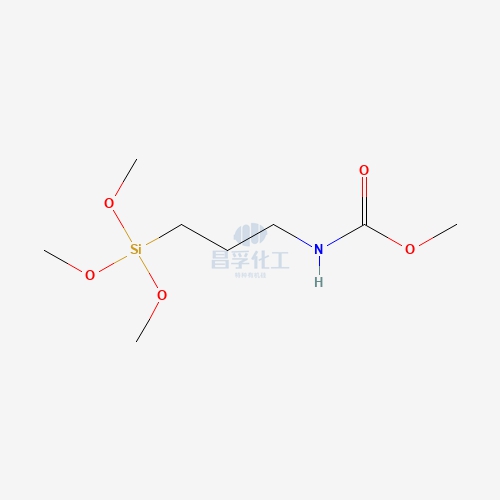
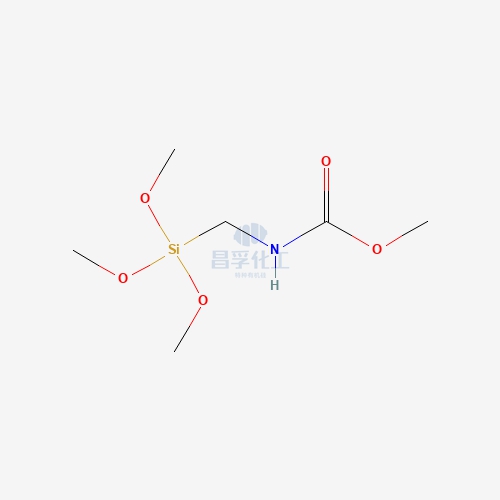
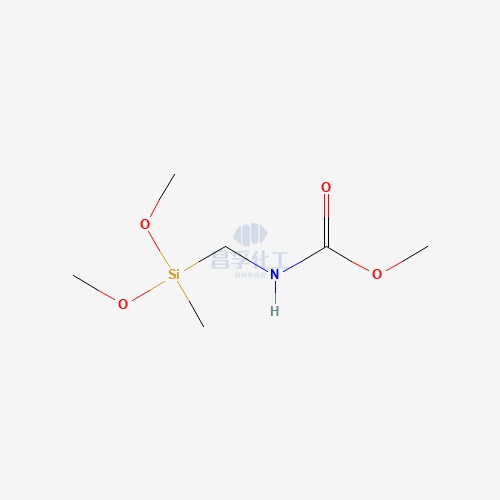
Popular Silicon Compounds
Popular Silicon Compounds
Related News & Blog
Related News & Blog






























































































+86 27 8439 6550
+86 181 6277 0058
sales@cfsilanes.com
Optics Valley Bio-City
No. 666, Gaoxin Avenue
Hongshan District, Wuhan City

+86 27 8439 6550 | +86 181 6277 0058
sales@cfsilanes.com
Optics Valley Bio-City
No. 666, Gaoxin Avenue
Hongshan District, Wuhan City
Copyright © Hubei ChangFu Chemical Co., Ltd. All Rights



![N-[5-(Trimethoxysilylpropyl)-2-aza-1-oxopentyl]caprolactam CAS: 106996-32-1 106996 32 1 N-[5-(Trimethoxysilylpropyl)-2-aza-1-oxopentyl]caprolactam CAS: 106996-32-1 106996 32 1](https://cdn.yofishseo.com/1363882761272232/106996-32-1.jpg)